Algebra 1 Test 392 Part 2 f(x)= 9x^3 2x^2 − 5x 4 and g(x) = 5x^3 −7x 4 what is f(x)−g(x)?Example f(x) = 2x3 and g(x) = x 2 "x" is just a placeholder To avoid confusion let's just call it "input" f(input) = 2(input)3 g(input) = (input) 2 Let's start (g º f)(x) = g(f(x)) First we apply f, then apply g to that result (g º f)(x) = (2x3) 2 What if we reverse the order of f and g?Math Input NEW Use textbook math notation to enter your math Try it

Find 1 Gof And 2 Fog Where F X X 2 G X X 2 3x 1 Youtube
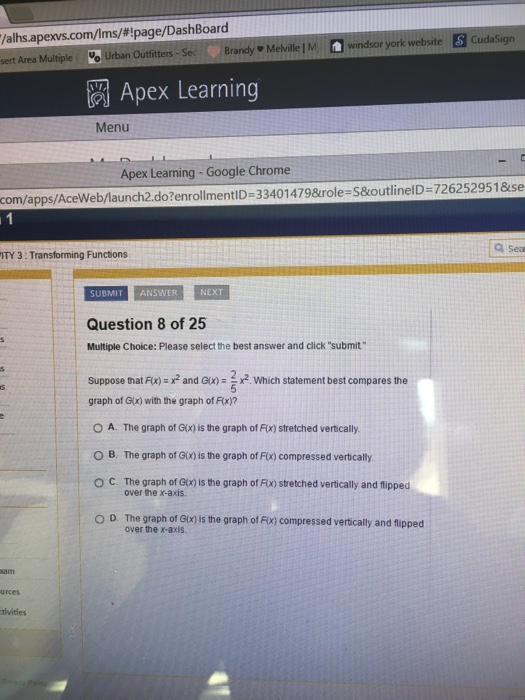
Suppose that f(x)=x^2 and g(x)=2/5x^2 which statement best compares
Suppose that f(x)=x^2 and g(x)=2/5x^2 which statement best compares-If {eq}f(x) = x^2 {/eq} and {eq}g(x) = x 1 {/eq}, what is {eq}f(g(x)) {/eq}?Get stepbystep solutions from expert tutors as fast as 1530 minutes Your first 5 questions are on us!
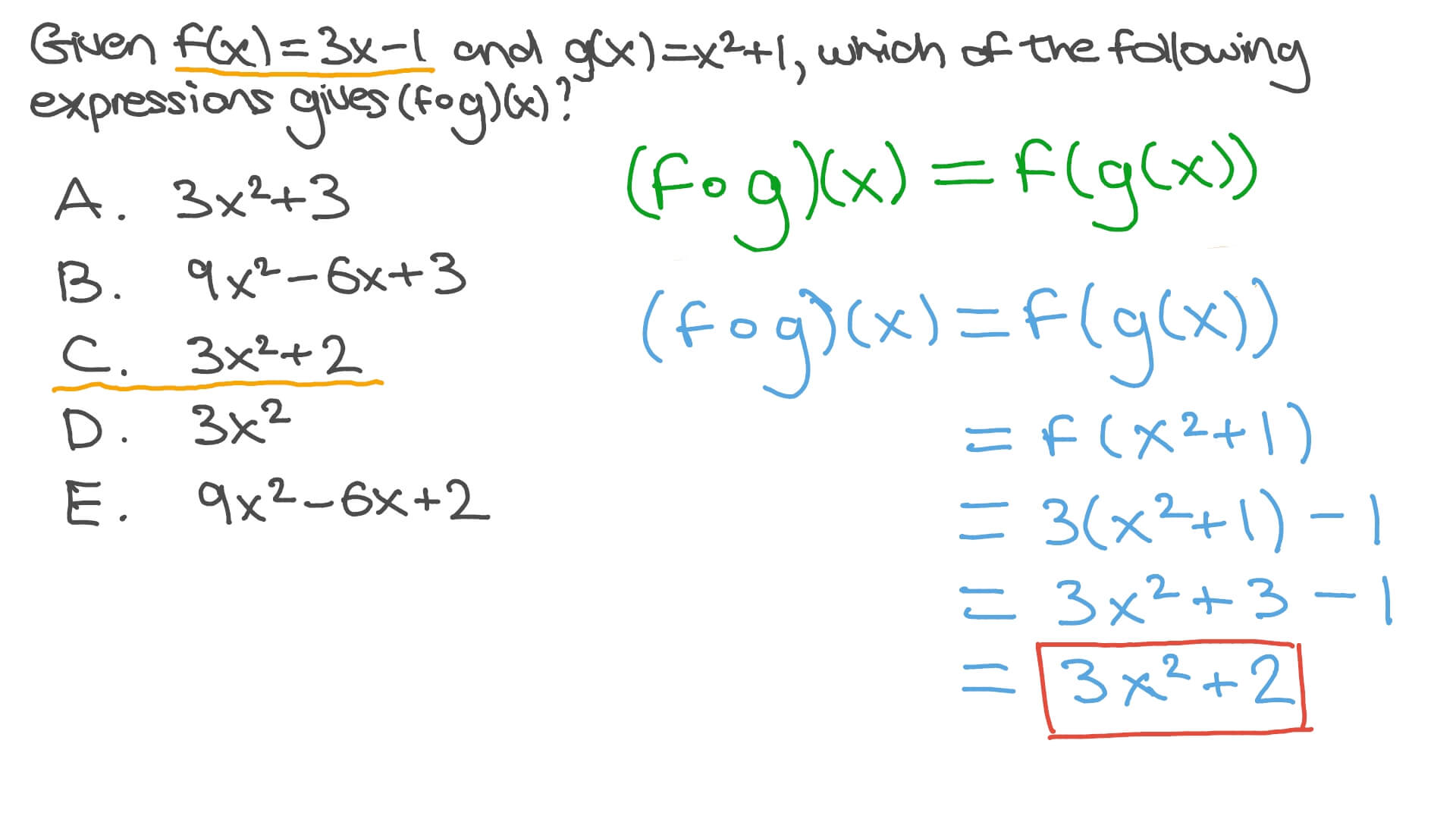



Question Video Finding The Composite Of Two Functions Nagwa
1 What is (f−g)(x)?Compute answers using Wolfram's breakthrough technology & knowledgebase, relied on by millions of students & professionals For math, science, nutrition, history From the given graph it is clear that the vertex of f(x) and g(x) are same, ie,(0,0) But the graph of g(x) compressed vertically If k>1, then graph of g(x) stretched vertically and if k
(f@g)(0)=2 >"substitute "g(x)=4x1" into "f(x) rArrf(4x1) =(4x1)^23(4x1) =16x^28x112x3 =16x^24x2 rArr(f@g)(x)=16x^24x2 "to evaluate "(f@g)(0)" substituteF (g (2)), g (x)=2x1, f (x)=x^2 \square!Now, that last example is not to be said it can't be done, but it involves completing the square to obtain f(x) = (x2) 2 2, then inversing it so that you get f1 (x) = 2sqrt(x2) However, there is another way that doesn't rely so much on informality and will work whether or not you can figure out exactly what you did with exactly one x
F(x)=x 4 −x 2 9 g(x)=x 3 3x 2 12 2 What is (f⋅g)(x)?It is not clear what the limit is Let g(x) = cos x^2, f(x) = √x , and α, β (α < β) be the roots of the quadratic equation 18x^2 – 9πx π^2 = 0 asked in Mathematics by Nisa (598k points) jee;




If F X Sqrt X 2 1 G X X 1 X 2 1 And H X 2x 3 Then Find F Prime H Prime G Prime X




Find A F G B F G C Fg And D F G And Chegg Com
BL Srivastava Answered 2 years ago Author has 46K answers and 21M answer views This is simple provided you know about the composition of functions Here f (x) = 2x 5 = y (let), then g (f (x)) = g (y) = cos (y/2) 3y = cos ( (2x 5)/2) 3 (2x 5) = cos (x 5/2) 6x 15 114K viewsIf a horizontal line intersects the graph of f(x) in more than one point, then f(x) is not onetoone The reason f(x) would not be onetoone is that the graph would contain two points that have the same second coordinate – for example, (2,3) and (4,3) That would mean that f(2) and f(4) both equal 3, and onetoone0 votes 1 answer Let u be a vector coplanar with the vectors a=2i3jk and vector b= jk If vector u is perpendicular to vector a and vector ub=24,




7 If F X And G X X2 2x Find Fg X And Its Chegg Com




F X X 2 What Is G X Brainly Com
Or the value of the function evaluated at 2x Giving a name f to a function for the function using independant variable x will be named as f (x), to be read, "the function f of x" Shown alone, f and x are not factors, but are a complete nameL'Hopital's Rule Consider the limit lim x → a f(x) g(x) If both the numerator and the denominator are finite at a and g(a) ≠ 0, then lim x → a f(x) g(x) = f(a) g(a) lim x → 3 x2 1 x 2 = 10 5 = 2 But what happens if both the numerator and the denominator tend to 0?F(g(x))=(1/x1)21 No solutions found Rearrange Rearrange the equation by subtracting what is to the right of the equal sign from both sides of the equation f(g(x))=(1/x1)21 No solutions found Rearrange Rearrange the equation by subtracting what is to the right of the equal sign from both sides of the equation




Find 1 Gof And 2 Fog Where F X X 2 G X X 2 3x 1 Youtube




Quantitative Aptitude Algebra Functions Let F X X 2 And G X 2 X Handa Ka Funda Online Coaching For Cat And Banking Exams
The answer is x^39x^227x29First, take (x3) and plug it into F(x) From that you break up (x3)^3 into three binomial because it is a 3 degree, and then you tack the 2 along sideIn this video we learn about function composition Composite functions are combinations of more than one function In this video we learn about f(g(x)) and gEvery element x of GF(2) satisfies x 2 = x (ie is idempotent with respect to multiplication);
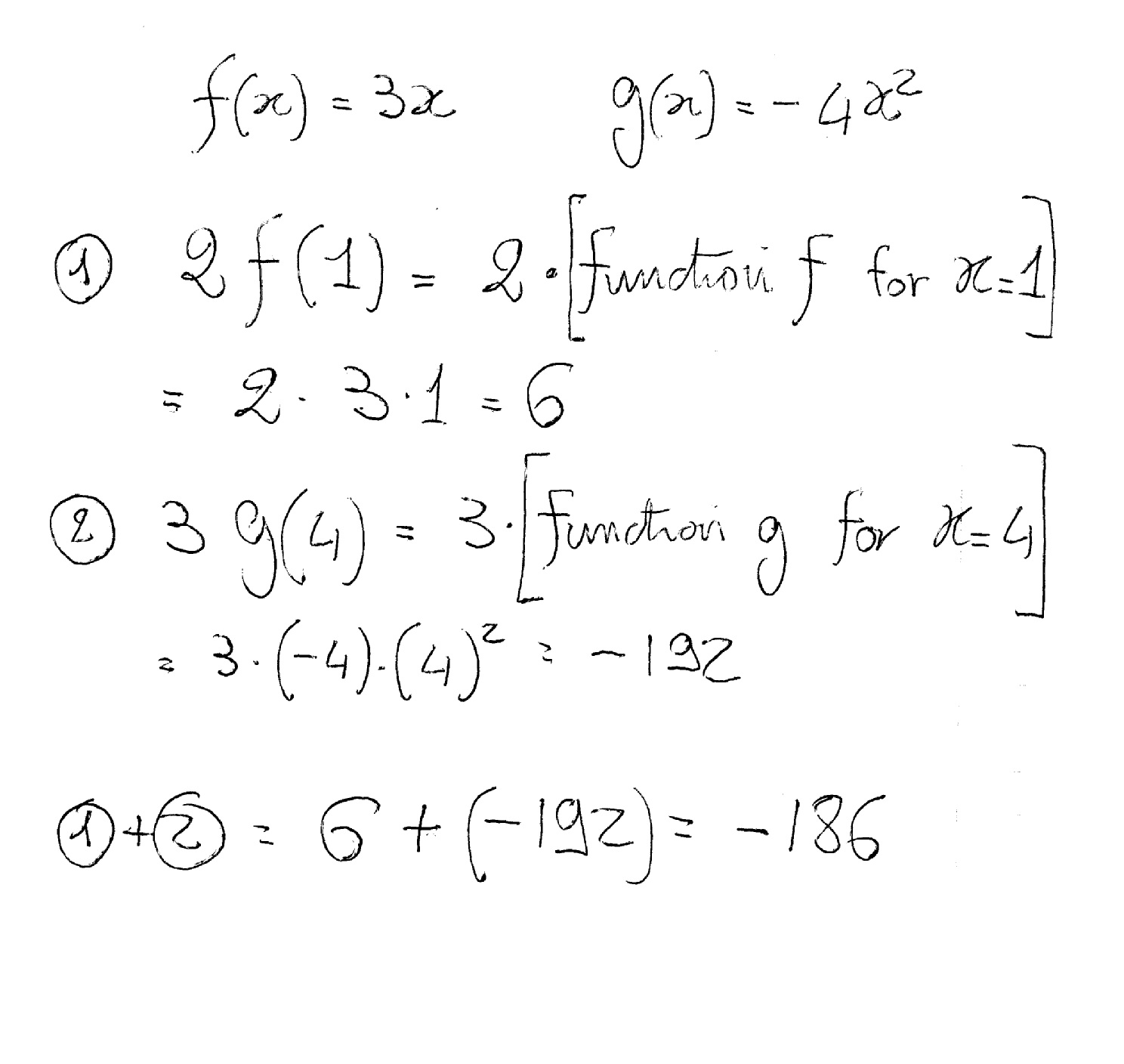



How Do Find The Value Of 2f 1 3g 4 If F X 3x And G X 4x 2 Socratic



Solving Equations Graphically
To find the answers, I can either work symbolically (like in the previous example) and then evaluate, or else I can find the values of the functions at x = 2 and then work from there It's probably simpler in this case to evaluate first, so f (2) = 2 (2) = 4 g (2) = (2) 4 = 6 h (2) = 5 – (2) 3 = 5 – 8 = –3Use "x" as the variable like this Examples sin(x) 2x−3;Axis of Symmetry x = 2 x = 2 Directrix y = −9 4 y = 9 4 Select a few x x values, and plug them into the equation to find the corresponding y y values The x x values should be selected around the vertex Tap for more steps Replace the variable x x with 1 1 in the expression f ( 1) = ( 1) 2 − 4 ⋅ 1 2 f ( 1) = ( 1) 2 4 ⋅ 1 2



Composite Functions Video Lessons Examples And Solutions



Secure Media Collegeboard Org Digitalservices Pdf Ap Apcentral Ap15 Calculus Ab Q2 Pdf
Get an answer for 'If f(x) = 2x3 and g(x) = x^2 2 find fog(x) and gof(x)' and find homework help for other Math questions at eNotes Search this site Go iconquestionSolution Steps g ( x ) = f ( x 2 ) 2 g ( x) = − f ( x 2) 2 Use the distributive property to multiply f by x2 Use the distributive property to multiply − f by x 2 \left (f\right)x2\left (f\right)2 ( − f) x 2 ( − f) 2 Multiply 2 and 1 to get 2 Multiply 2 and − 1 to get − 2Left 13 units, down 2 units right 13 units, down 2 units left 13 units, up 2 units right 13 units, up 2 units




F X X2 What Is G X Brainly Com




F X X 2 What Is G X Brainly Com
2*f (x) means two multiplied by the function f f (2x) means the function at 2x;Every element x of GF(2) satisfies x x = 0 and therefore −x = x;The expression $g^2(x)$ means $g(g(x))$ To write this out with your specific $g$, we get $$g(g(x)) = 3g(x) 1$$Now we substitute again $$g(g(x)) = 3g(x) 1 = 3(3x1) 1$$Then simplify that Share



Http Www Midwayisd Org Cms Lib Tx Centricity Domain 164 Preap alg ii 6 3 Pdf




F X X 2 What Is G X Brainly Com
Write f(x) = √5 − x2 as the composition of two functions Solution We are looking for two functions, g and h, so f(x) = g(h(x)) To do this, we look for a function inside a function in the formula for f(x) As one possibility, we might notice that the expression 5 − x2 is the inside of the square root= 2x 3 x 2 2 The domain of (f g)(x) consists of all xvalues that are in the domain of both f and g In this example, f and g both have domain consisting of all real numbers, therefore (f g)(x) also has domain consisting of all real numbers The Difference of Two Functions B (1/4x)^2 will widen the parabola C 4x^2 is too wide to be g(x) D (16x)^2 is too narrow to be g(x) A is the correct answer When graphed on desmos com / calculator it shows this is the correct answer I hope this helped!




F X X 2 What Is G X Brainly Com




F X X 2 What Is G X Brainly Com
Get an answer for 'If f(x)= 2/(x3) and g(x)= 1/x then what is (gof)(x)?' and find homework help for other Math questions at eNotesComposite Function A composite function is a function which is made by combining two or more than two functionsIf we replace x by g ( x), we then have f ( g ( x)) = 2 g ( x) 1 But we also know that g ( x) = x 2 − 2, so we Continue Reading A So we have f ( x) = 2 x 1 and g ( x) = x 2 − 2 That basically means that whatever the value of x, f ( x) = 2 x 1 Specifically, if x = g ( − 1), f ( g ( − 1)) = 2 g
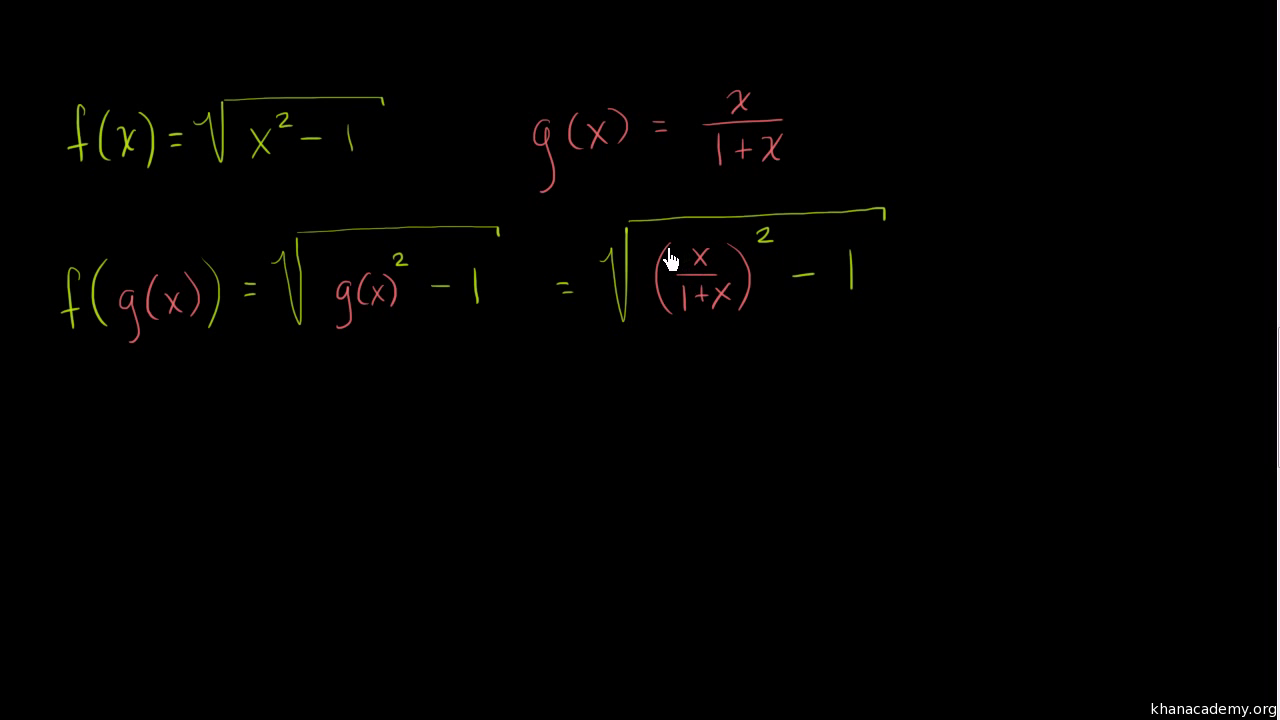



Finding Composite Functions Video Khan Academy




F X X 2 What Is G X Brainly Com
F(x)=x 2 2x−6 g(x)=x 4 3 3 jbouyer Ex 13, 6 Show that f −1, 1 → R, given by f(x) = 𝑥/(𝑥 2) is oneone Find the inverse of the function f −1, 1 → Range f (Hint For y ∈ RangeI'll give you a hint to get you started If




Please Help Suppose F X X 2 What Is The Graph Of G X 1 4 F X Brainly Com




F X X 2 What Is G X A G X X 2 4 B G X X 2 4 C G X 4x 2 D G X X 2 4 Brainly Com
1 Answer AJ Speller (f ∘ g)(x) = f (g(x)) = f (x 2) = (x 2)2 Click on the link below to see another example If f (x) = x2 and g(x) = x 2, what is (g ∘ f)(x)?SOLUTION Find (fg) (x), (fg) (x), (f*g) (x) and (f/g) (x) for each f (x) and g (x) 2 f (x)= 8x^2 g (x)=1/x^2 I'm having trouble understanding what i have to do, please help You can put this solution on YOUR website!Eq1) or equivalently if the following equation holds for all such x f (x) − f (− x) = 0 {\displaystyle f(x)f(x)=0} Geometrically, the graph of an even function is symmetric with respect to the y axis, meaning that its graph remains unchanged after reflection about the y axis Examples of even functions are The absolute value x ↦ x , {\displaystyle x\mapsto x,} x ↦ x 2




7 1 Operations On Functions Operationdefinition Ppt Download




Find The Following F X 2x 3 G X 2 X F Chegg Com
This means that the characteristic of GF(2) is 2;Then type x=6 Try it now 2x3=15 @ x=6 Clickable Demo Try entering 2x3=15 @ x=6 into the text box After you enter the expression, Algebra Calculator will plug x=6 in for the equation 2x3=15 2(6)3 = 15 The calculator prints "True" to let you know that the answer is Example 16 Let f(x) = x2and g(x) = 2x 1 be two real functions Find (f g) (x), (f – g) (x), (fg) (x), ("f" /𝑔) (x) f(x) = x2 & g(x) = 2x 1 (f g) (x) = f
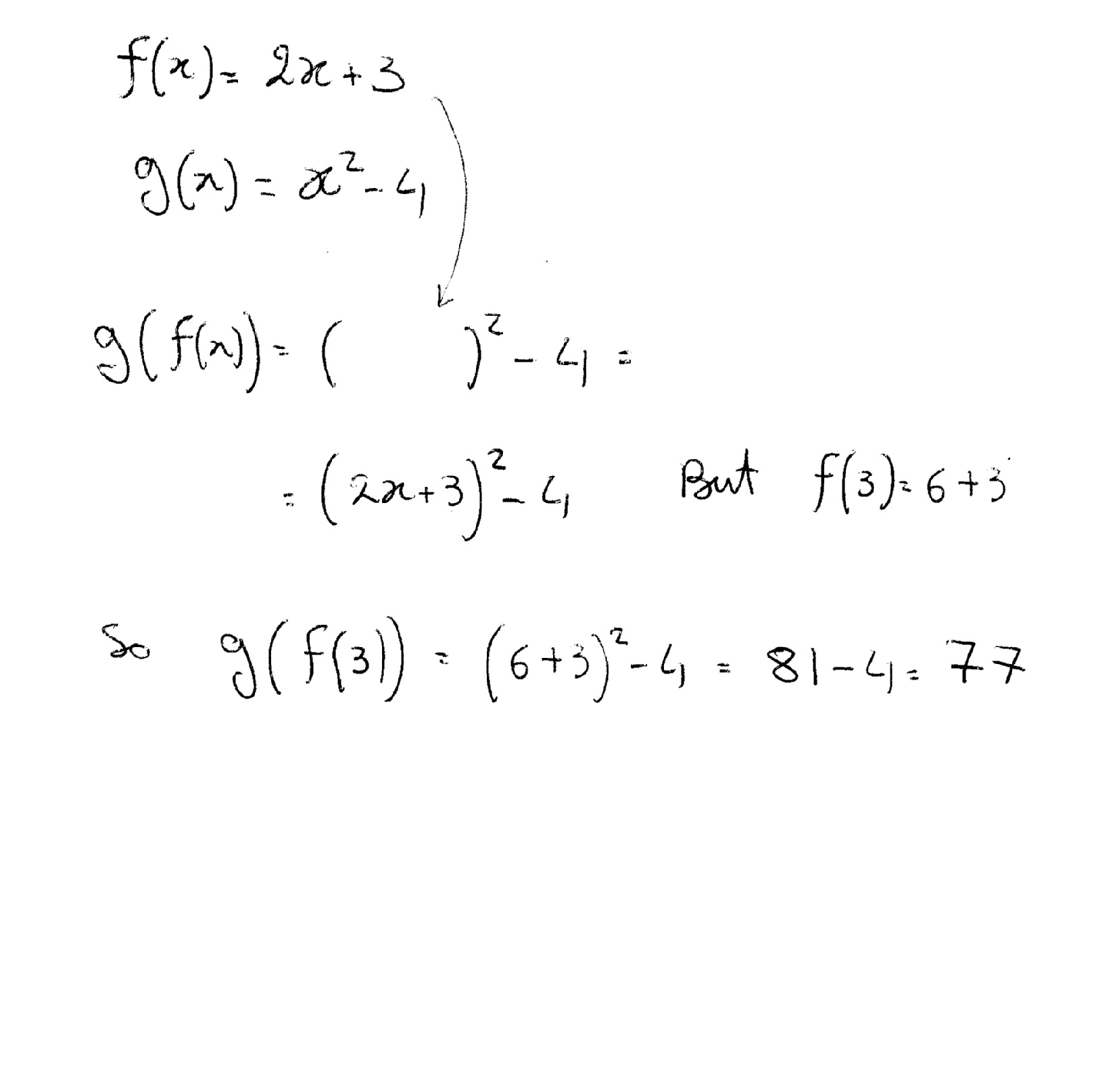



Let F X 2x 3 And G X X 2 4 And H X X 3 2 How Do You Find G F 3 Socratic
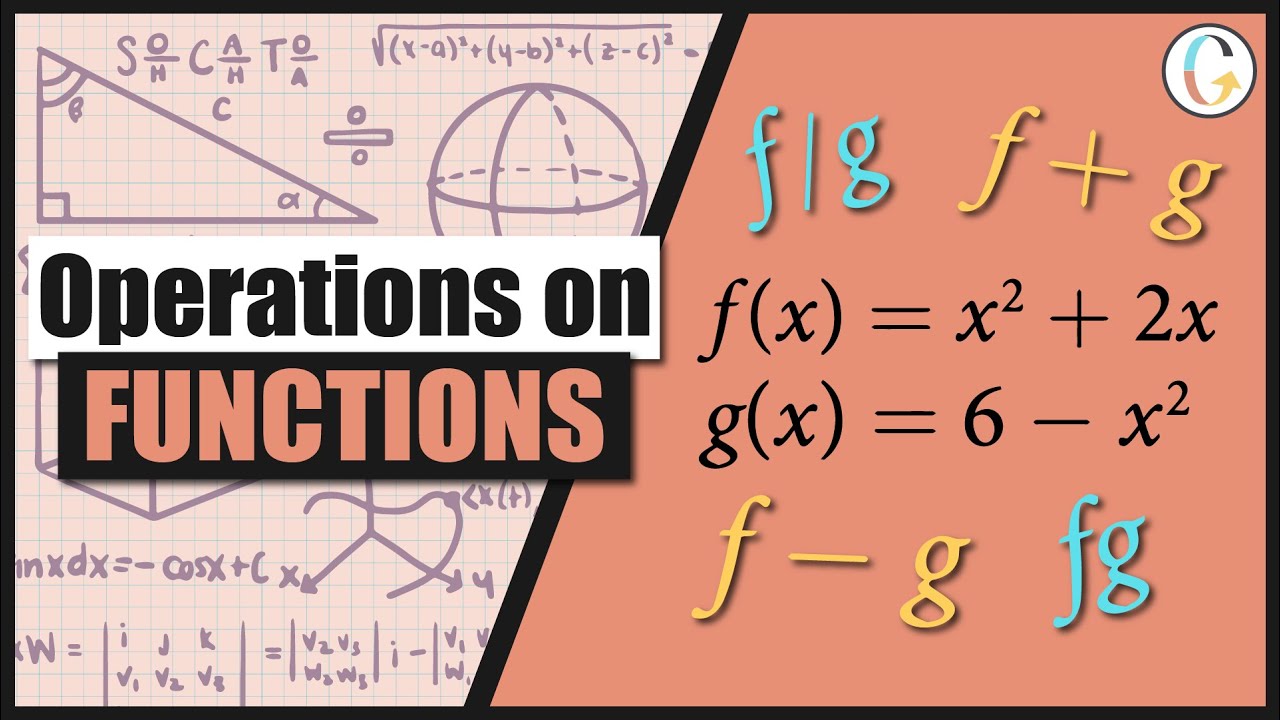



Given F X X2 2x And G X 6 X2 Find F G F G Fg And F G Youtube
And "( f o g)(x)" means "f (g(x))" That is, you plug something in for x, then you plug that value into g, simplify, and then plug the result into f The process here is just like what we saw on the previous page, except that now we will be using formulas to find values, rather than just reading the values from lists of points Given f(x) = 2xG*(x)(2*f*(x))=0 Step 1 Pulling out like terms 11 Pull out like factors gx 2xf = x • (g 2f) Equation at the end of step 1 Step 2 Theory Roots of a product 21 A product of several terms equals zero When a product of two or more terms equalsFree functions composition calculator solve functions compositions stepbystep



Solution If F X 2x 1 And G X X 2 Find 1 G G X 2 G F X 3 F G X 4 F F X




Suppose That We Have Two Functions F X And G X Chegg Com
Answer to if f(x)=2x^2 and g(x)=1/x2 , find a) fg b) gf c)ff d) gg By signing up, you'll get thousands of stepbystep solutions to yourCos(x^2) (x−3)(x3) Zooming and Recentering To zoom, use the zoom slider To the left zooms in, to the right zooms out When you let go of the slider it goes back to the middle so you can zoom moreShow all of your steps and write your final answer in factored form
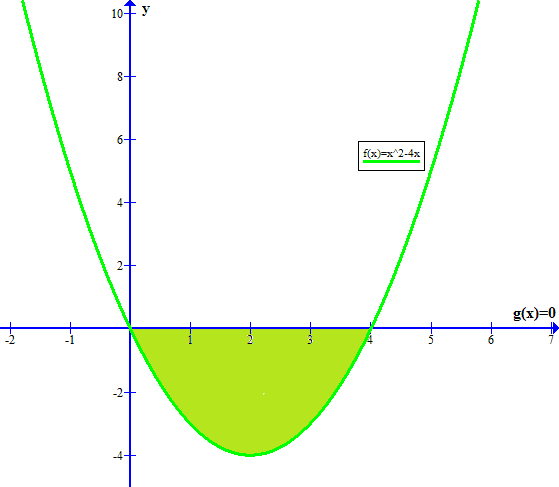



How Do You Find The Area Between F X X 2 4x G X 0 Socratic




Question 1 A For F X 2 2 1 G X X 1 Find Fg Chegg Com
Given the functions, f(x) = x2 2 and g(x) = 4x 1, perform the indicated operation When applicable, state the domain restriction g(f(x)) 4 x2 1 16 x2 3 4 x2 7 16 x2 8 x 3 Please help I thinks that it is 16 x2 3 If g(x) = x2 x 1 and (gof)(x) = 4x2 10x 5, then f(5/4) is equal to (1) 3/2 (2) 1/2 (3) 3/2 (4) 1/2 Welcome to Sarthaks eConnect A unique platform where students can interact with teachers/experts/students to get solutions to their queriesFind (g o f) (2x)
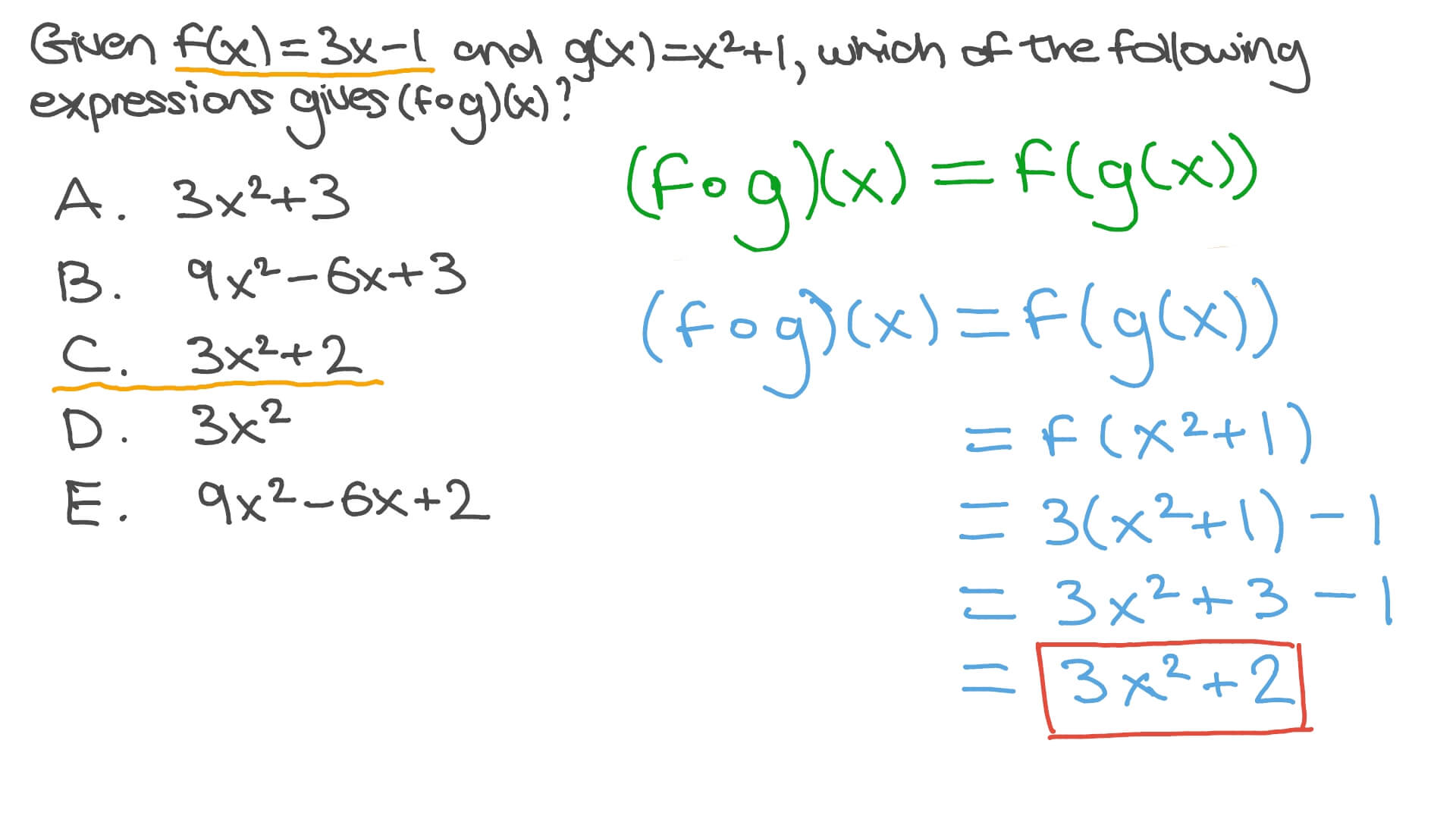



Question Video Finding The Composite Of Two Functions Nagwa



Http Www Cusd80 Com Cms Lib6 Az Centricity Domain 2148 Q1 exam review 13 14 key pdf Pdf
Evaluate g(f (x)) g ( f ( x)) by substituting in the value of f f into g g g(x−2) = (x−2)2 g ( x 2) = ( x 2) 2 Combine the opposite terms in (x− 2)2 ( x 2) 2 Tap for more steps Add − 2 2 and 2 2 g ( x − 2) = x 0 g ( x 2) = x 0 Add x x and 0 0 g ( x − 2) = x g ( x 2) = xStart studying Evaluating Functions Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study toolsCalculate (f ∘ g) (x) using f(x) = 2x 3 and g(x) = x 2 1, Solution (f ∘ g) (x) = f(g(x)) = 2 (g(x)) 3 = 2(x 2 1) 3 = – 2 x 2 5 Example 10 Given f(x) = √ (x 2) and g(x) = ln (1 – x 2), find domain of (g ∘ f) (x) Solution (g ∘ f) (x) = g(f(x)) ln (1 – f(x) 2) = ln (1 – √ (x 2) 2) ln (1 – (x 2))



Secure Media Collegeboard Org Digitalservices Pdf Ap Apcentral Ap15 Calculus Ab Q2 Pdf




1 Given The Functions F X X 1 And G X 3 X Chegg Com
Justine graphs the function f(x) = (x 7)2 1 On the same grid, she graphs the function g(x) = (x 6)2 3 Which transformation will map f(x) on to g(x)?Y = f(x) = x^2 means the independent variable in the equation is x y = f(a) = a^2 means the independent variable in the equation is a the rules are the same the only difference is the variable that the equation is working with that is why when you say f(x) = x^2, f(x) becomes the dependent variable and x is the independent variable2 3 x y g(x) = 3 x2 f(x) = x2 1 Using the washer method, the volume integral is p Z 1 1 g(x)2 f(x)2 dx = p Z 1 1 (3 x2)2 (x2 1)2 dx 1(b) (5 points) Write the integral for the volume of the solid of revolution obtained by rotating this region about the line x = 3 Do not evaluate the integral SOLUTION Now using the shell method, the




F X X 2 What Is G X A G X 1 4x 2 B G X 1 2x 2 C G X 2x 2 D G X 1 2x 2 Check Picture Brainly Com



Secure Media Collegeboard Org Digitalservices Pdf Ap Apcentral Ap15 Calculus Ab Q2 Pdf
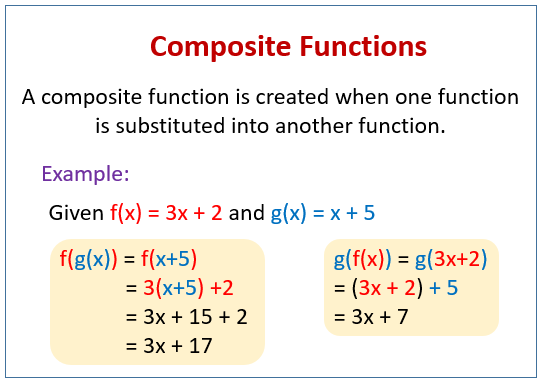
(f º g)(x) = f(g(x)) First we apply g, then apply f to that resultFirst write the composition in any form like \( (go f) (x) as g (f(x)) or (g o f) (x^2) as g (f(x^2))\) Put the value of x in the outer function with the inside function then just simplify the function Although, you can manually determine composite functions byThis is an instance of Fermat's little theorem GF(2) is the only field with this property (Proof if x 2 = x, then either x = 0 or x ≠ 0
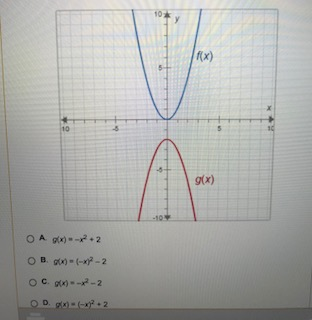



The Functions F X And G X Are Shown On The Graph Chegg Com




F X X 2 What Is G X Brainly Com



Suppose That F X X 2 And G X 2 5 X 2 Which Chegg Com




1 Let F X X2 1 And G X 3x A Evaluate Chegg Com




If F X 3x 2 And G X X 2 Then Fog X Youtube




F X X 2 What Is G X Brainly Com
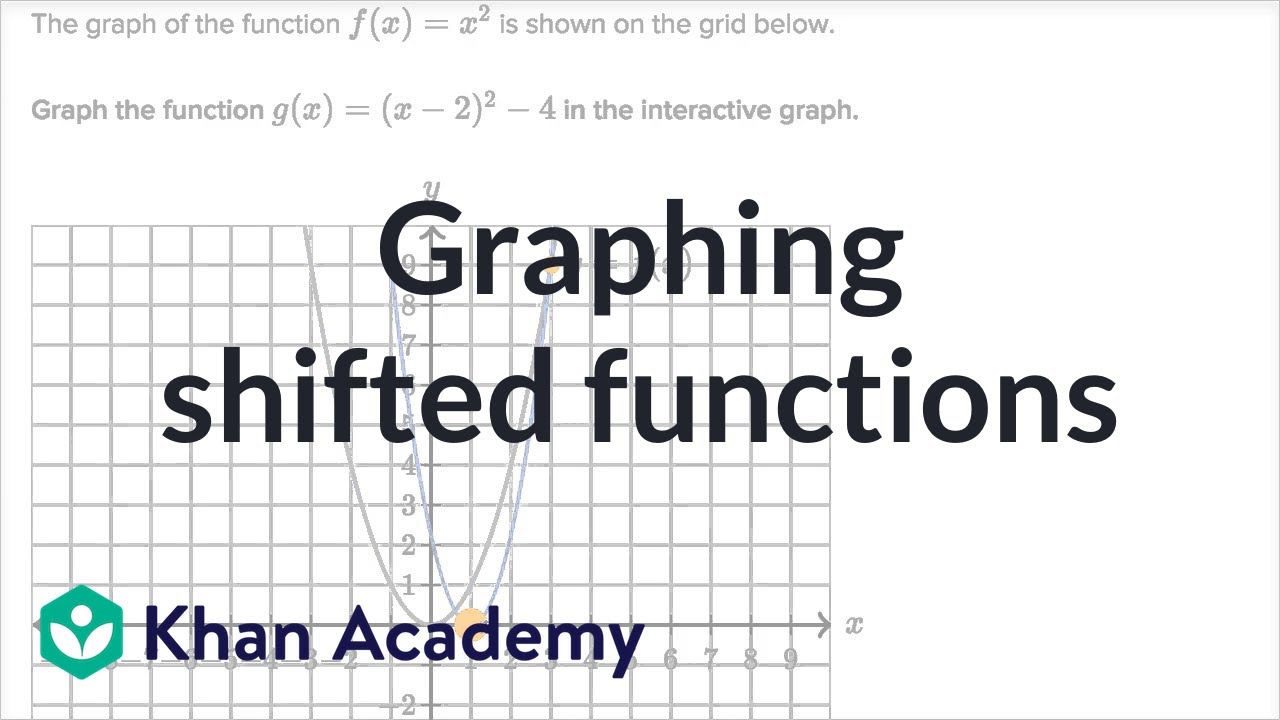



Graphing Shifted Functions Video Khan Academy




F X X 2 What Is G X Brainly Com



Efisd Net Common Pages Displayfile Aspx Itemid




F X X 2 What Is G X Brainly Com




F X X2 What Is G X Brainly Com



Manipulating Graphs



Http Smacmathapcalculus Weebly Com Uploads 1 9 2 5 Fc Unit 3 1 Hw Key V2 Pdf




F X X 2 What Is G X Brainly Com
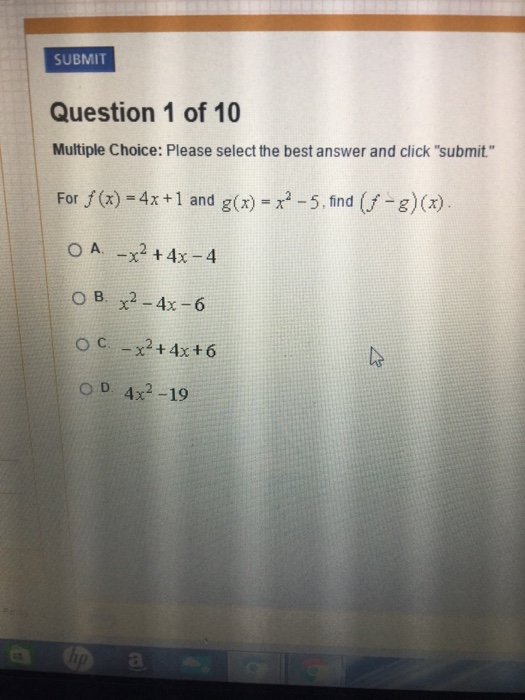



For F X 4x 1 And G X X 2 5 Find F G X Chegg Com




J J Allu G X El 4 Let F X X And G X 3x Chegg Com




1 Let F X X2 1 And G X 3x A Evaluate Chegg Com




F X X 2 What Is G X Brainly Com



How Do You Find The Area Between F X X 2 2x 1 G X 3x 3 Socratic



Http Math Colorado Edu Nita Someexam2practicesol Pdf



Www3 Nd Edu Apilking Math Work Old exams Exam1f08soluutions Pdf
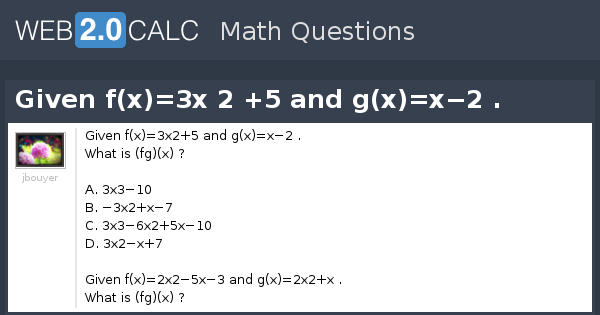



View Question Given F X 3x 2 5 And G X X 2
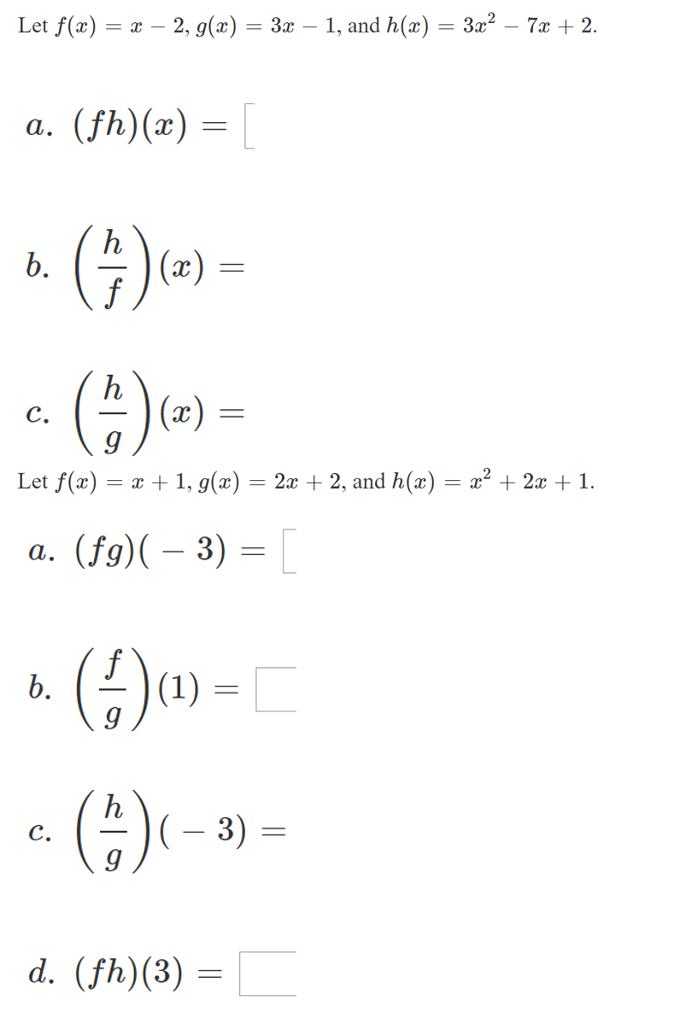



Let F X X 2 G X 3x 1 And H X 3x 2 7x Chegg Com




The Functions F X And G X Are Shown On The Graph F X X2 What Is G X A G X X2 2 B G X Brainly Com




F X X 2 What Is G X Brainly Com
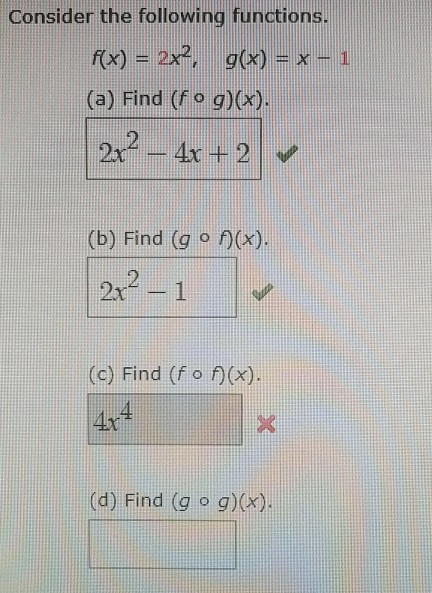



Consider The Following Functions X 2x2 A Chegg Com



Www Nhvweb Net Nhhs Math Psorg Files 11 08 Answers To 5 4 Function Operations Pdf




Precalculus Concepts Concavity Expii




Function Composition Given F X 2x 2 And G X 2 Find F ºg X F ºg X F G X Start On The Inside F G X G X 2 So Replace It F G X F 2 Ppt




Let F Be The Function Defined By F X X 3 X If G X Is The Inverse Of F X And G 2 1 What Is The Value Of The Derivative Of G At X 2




Find The Greatest Common Divisor Of F X 2x 3 2x 2 X 4 And G X X 4 3x 3 4x 2 3x Mathematics Stack Exchange
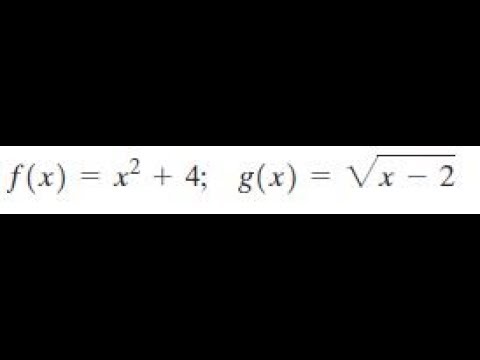



F X X 2 4 G X Sqrt X 2 Youtube




If F X X 2 And G X 2x Then Evaluate I F G 3 Ii F G 2 Iii F G 1 Iv F G 5




F X X 2 What Is G X Brainly Com
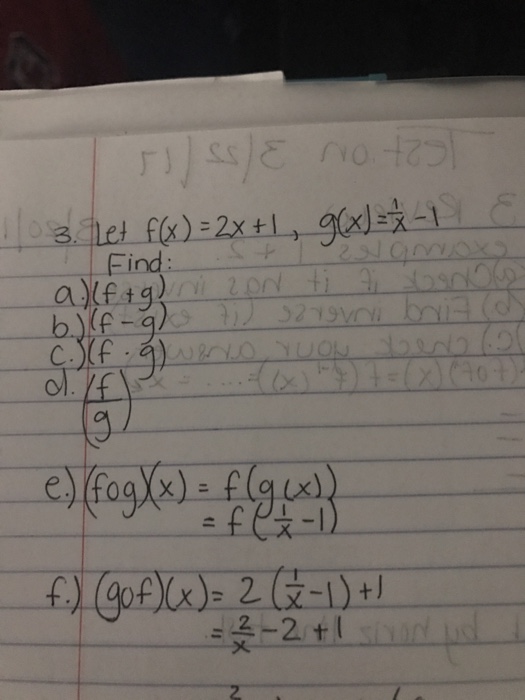



Let F X 2x 1 G X 1 X 1 Find A F G Chegg Com



Suppose F X X 2 What Is The Graph Of G X 1 3f X



F X X 2 What Is G X 1 9



F X 3x 2 G X 2x 2 1 Youtube




If F X 2x And G X X 2 2 1 Then Which Of The Following Can Be Discontinuous Function Youtube
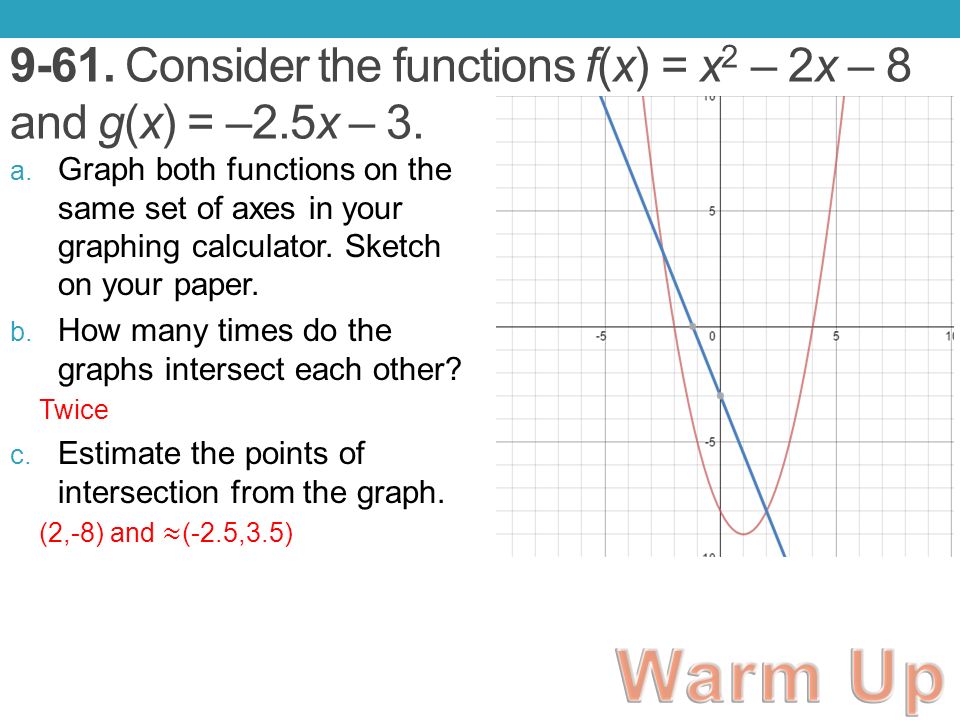



9 61 Consider The Functions F X X 2 2x 8 And G X 2 5x Ppt Download



Www Manhassetschools Org Site Handlers Filedownload Ashx Moduleinstanceid 4085 Dataid Filename Aimm 27 with key Pdf
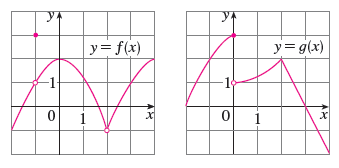



Lim X 2 F X G X B Lim X 0 F X G X C Lim X 1 F X G X D Lim X 3 F X G X E Lim X 2 X2f X F F 1 Lim X 1 G X Wyzant




Example 16 Let F X X2 And G X 2x 1 Find F G Fg F G
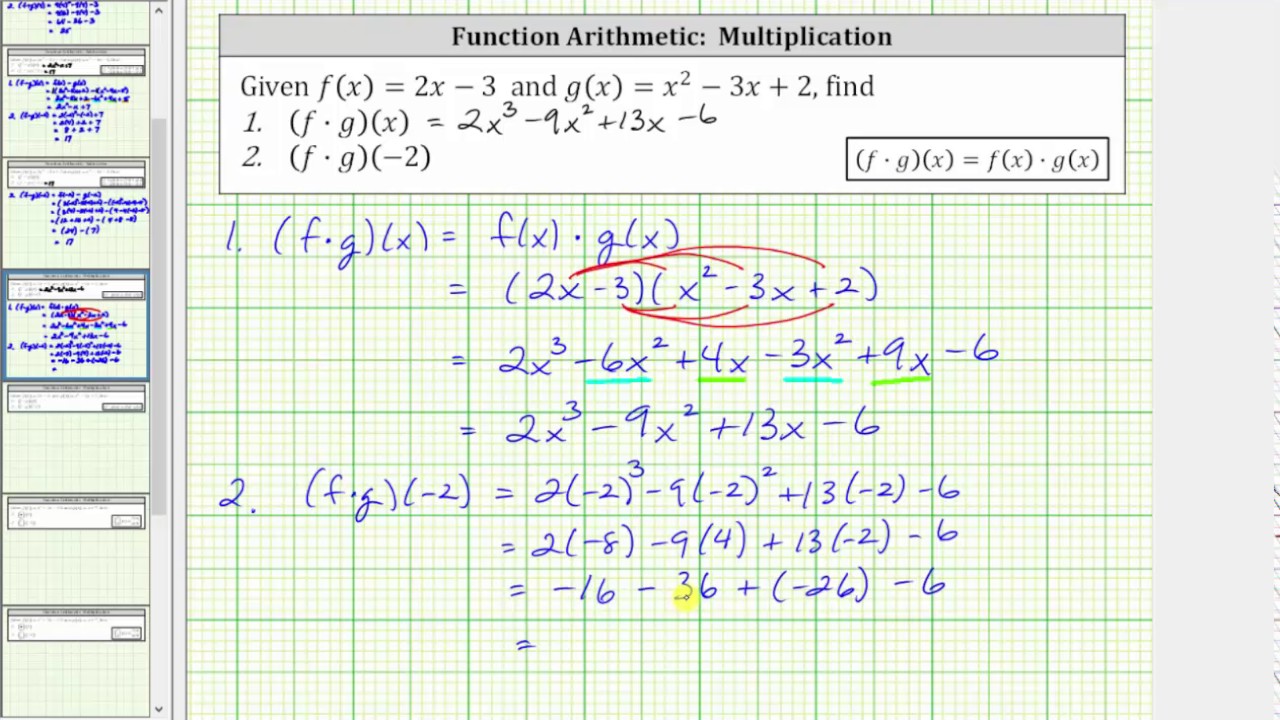



Function Arithmetic Product F G X And F G 2 Youtube




Given That F X 2 X 4 And G X 3 X 5 Find Gf 3 With Noob Like Steps Please I Need A Really Clear Working To Fully Understand Thanks 3 Socratic
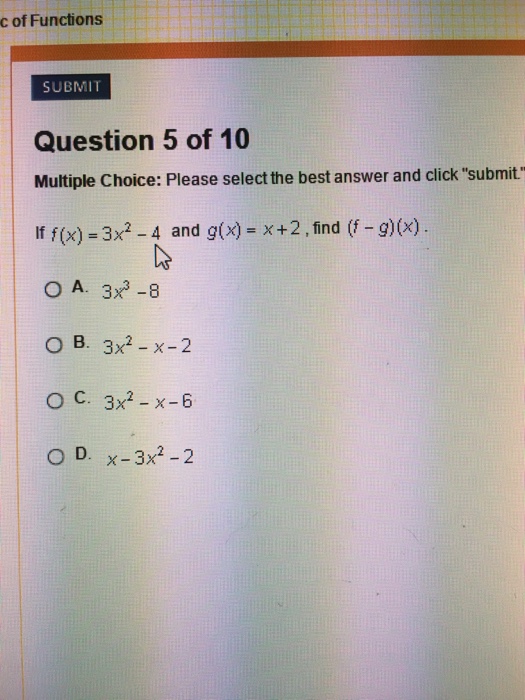



If F X 3x 2 4 And G X X 2 Find F G X Chegg Com




Function Transformations Algebra Ii Quiz Quizizz




F X X2 What Is G X F X G X 2 2 15 Brainly Com




Please Help F X X 2 What Is G X Brainly Com




F X X2 What Is G X Brainly Com




Please Help Me F X X2 What Is G X Brainly Com



What Is The Area Of The Region Enclosed By The Graphs Of F X X 2x 2 And G X 5x Quora




Verifying Inverse Functions By Composition Not Inverse Video Khan Academy




Answered Consider The Following Functions F X Bartleby



Are Inverses F X



Suppose F X X 2 And G X 1 4x 2
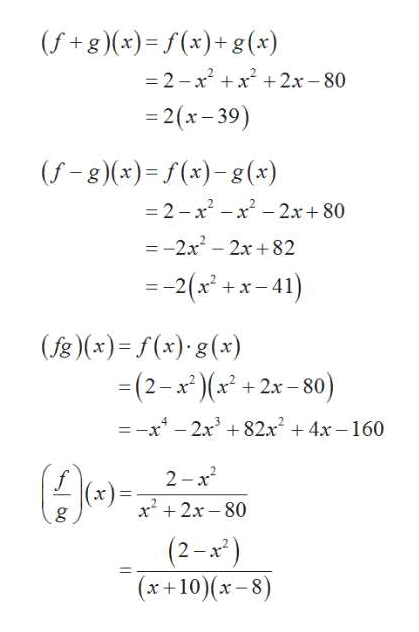



Answered For The Functions F X 2 X2 And G X X2 Bartleby



How Do You Draw F X 2x 2 And G X 2x 4 On The Same Graphs Socratic



F X X 2 What Is G X Apex




F X X2 What Is G X Brainly Com



1 3 Let F X X2 7 And G X X 3 Find The Chegg Com
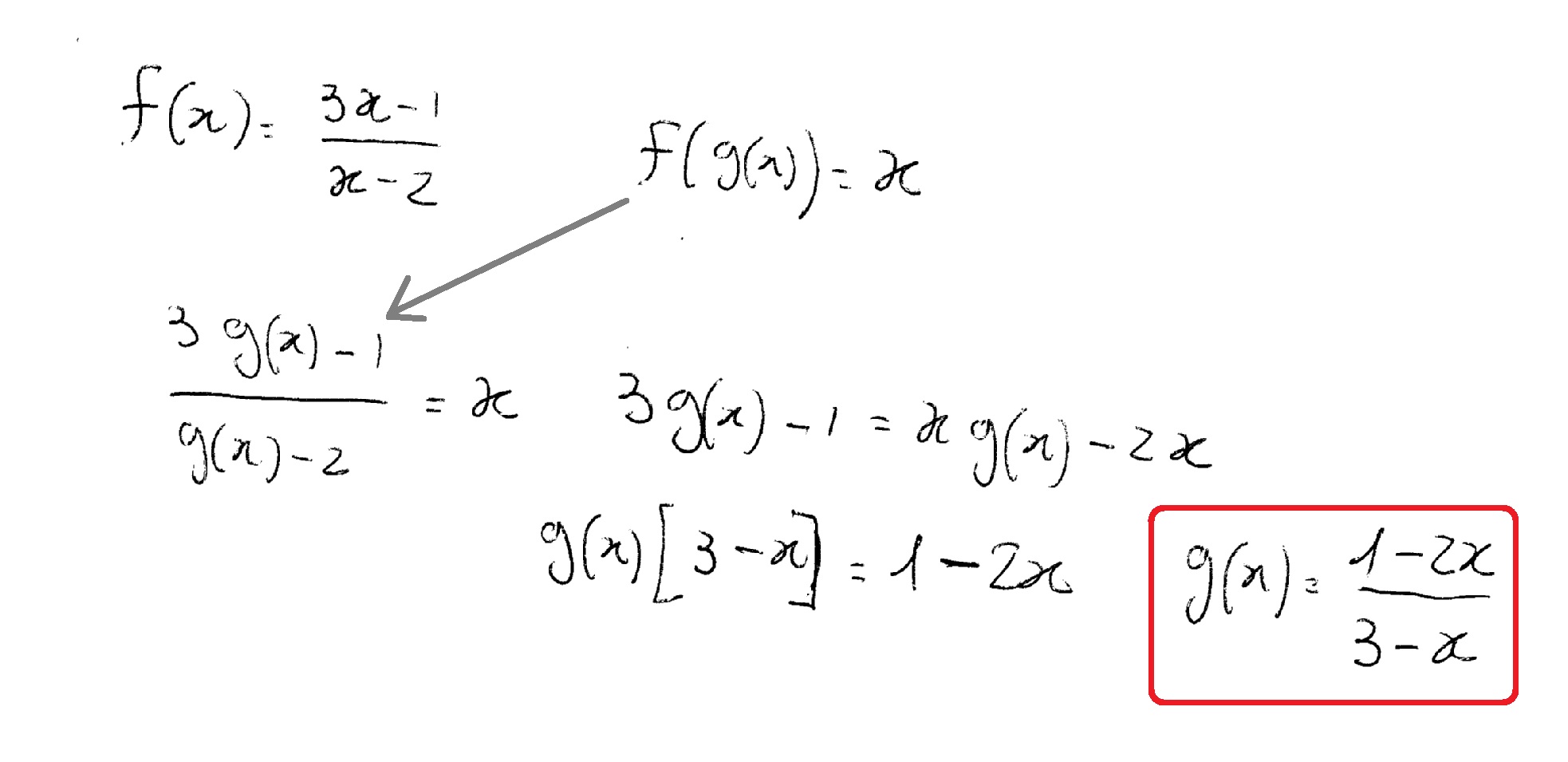



Let F X 3x 1 X 2 And F G X X How Do You Find G X Socratic



Www Humbleisd Net Cms Lib2 Tx Centricity Domain 3611 Answer review final exam fall Pdf



Math Scene Equations Iii Lesson 3 Quadratic Equations
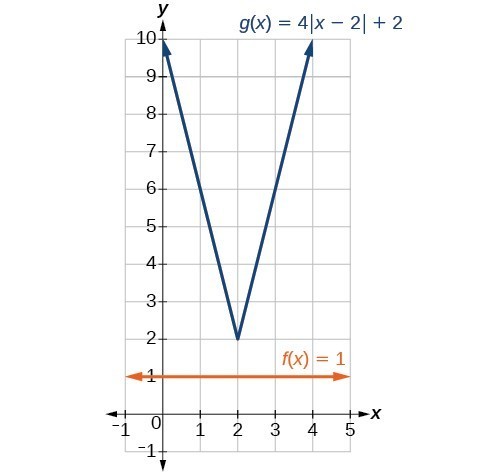



Solve An Absolute Value Equation College Algebra




Answer The Following If F X X 2 2 And G X Chegg Com



Solution The Function F X X2 The Graph Of G X Is F X Translated To The Left 6 Units And Down 5 Units What Is The Function Rule For G X




View Question Please Help
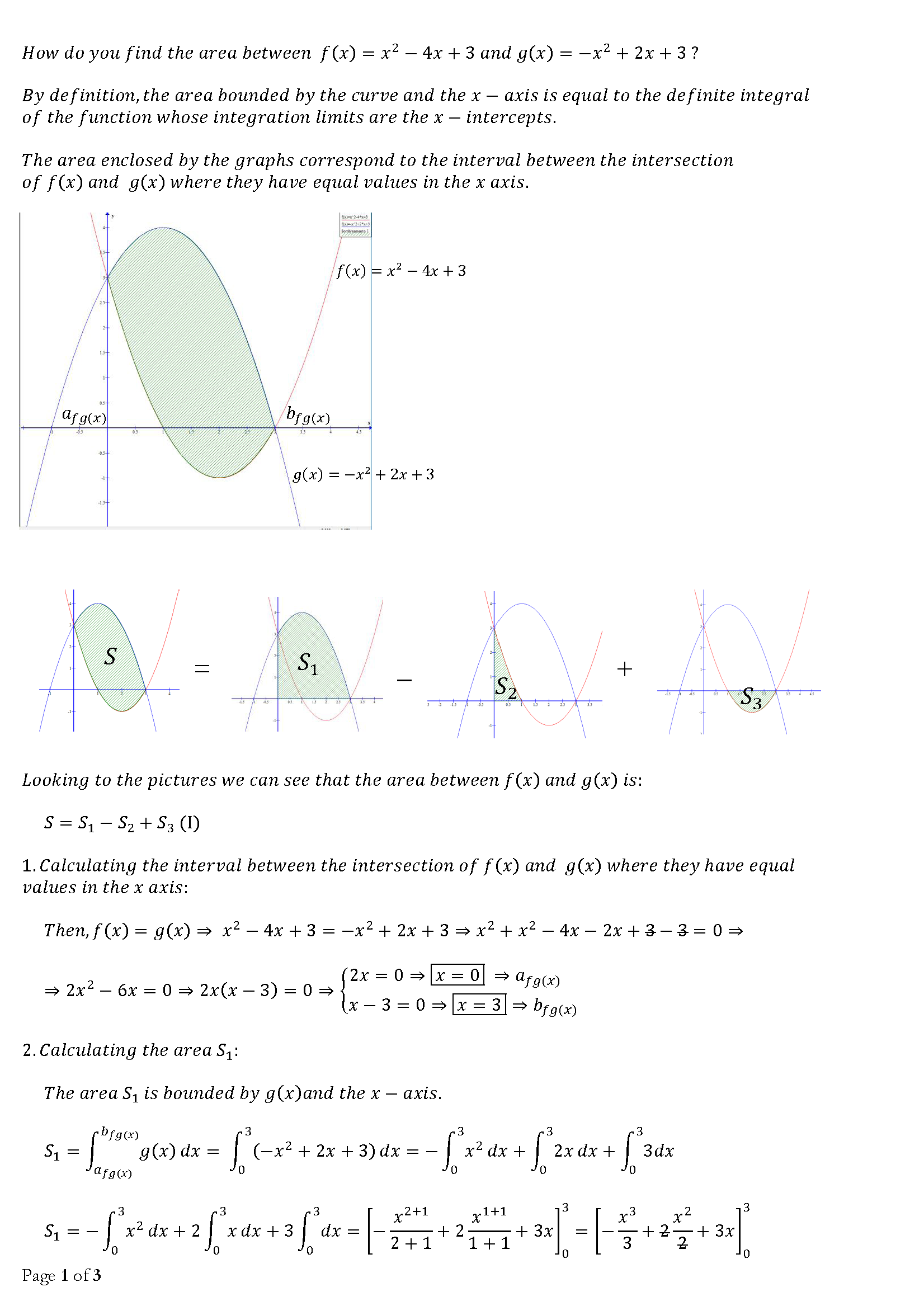



How Do You Find The Area Between F X X 2 4x 3 And G X X 2 2x 3 Socratic



F X 2x 3 5x 2 G X 2x 1 Find F G X Youtube


